Scenarios Analysis
1. Wind Vector & Temperature Contour
2. Vertical Temperature Contour
3. Wind Contour (U-wind, W-wind)
4. Average Temperature Series
1. Wind Vector & Temperature Contour
current (2024)
SSP2-4.5 (2100)
SSP5-8.5 (2100)
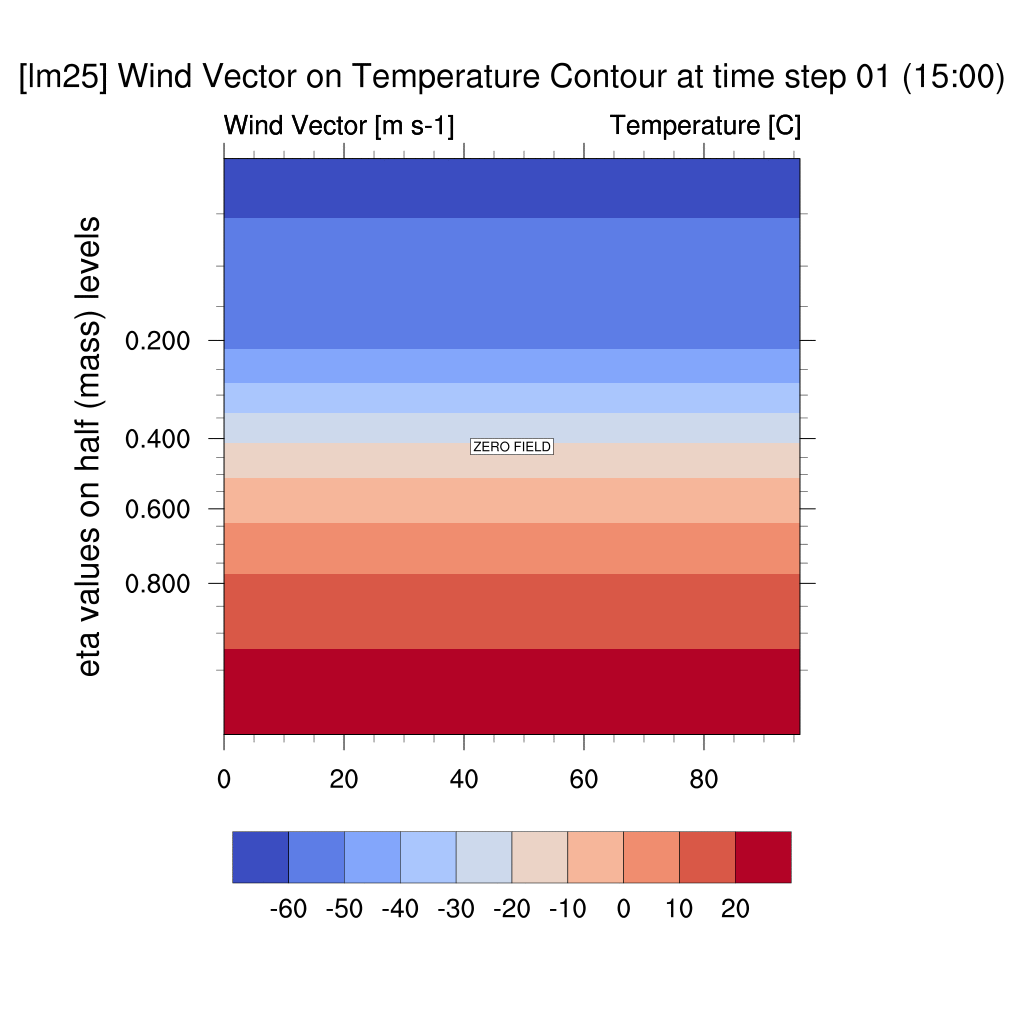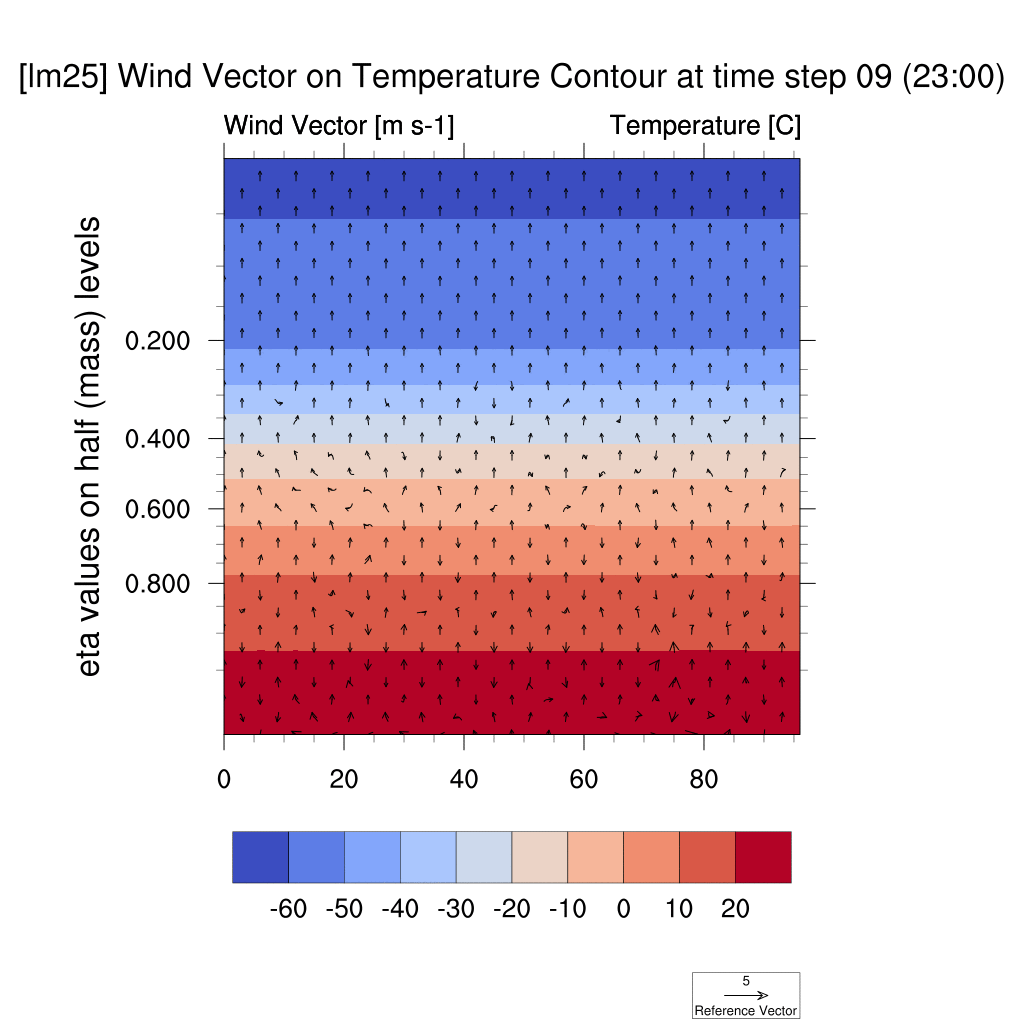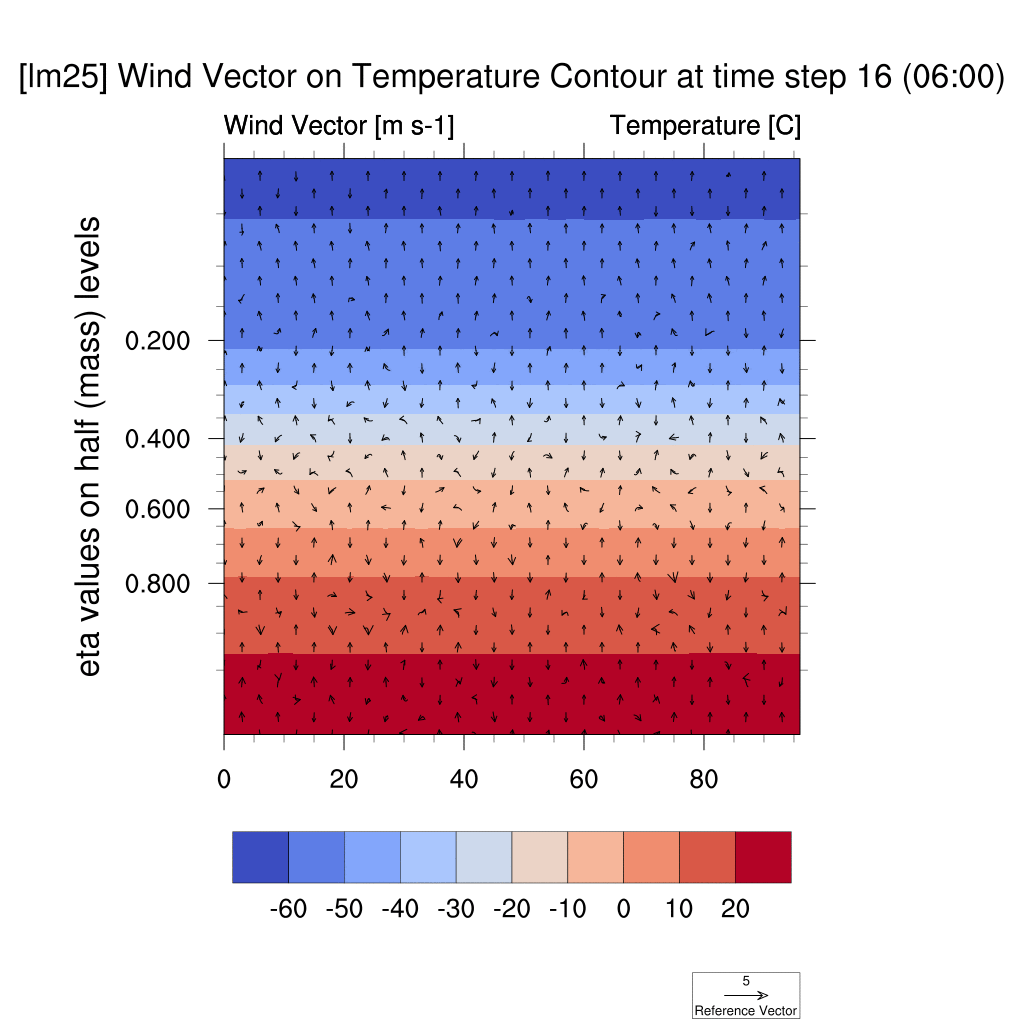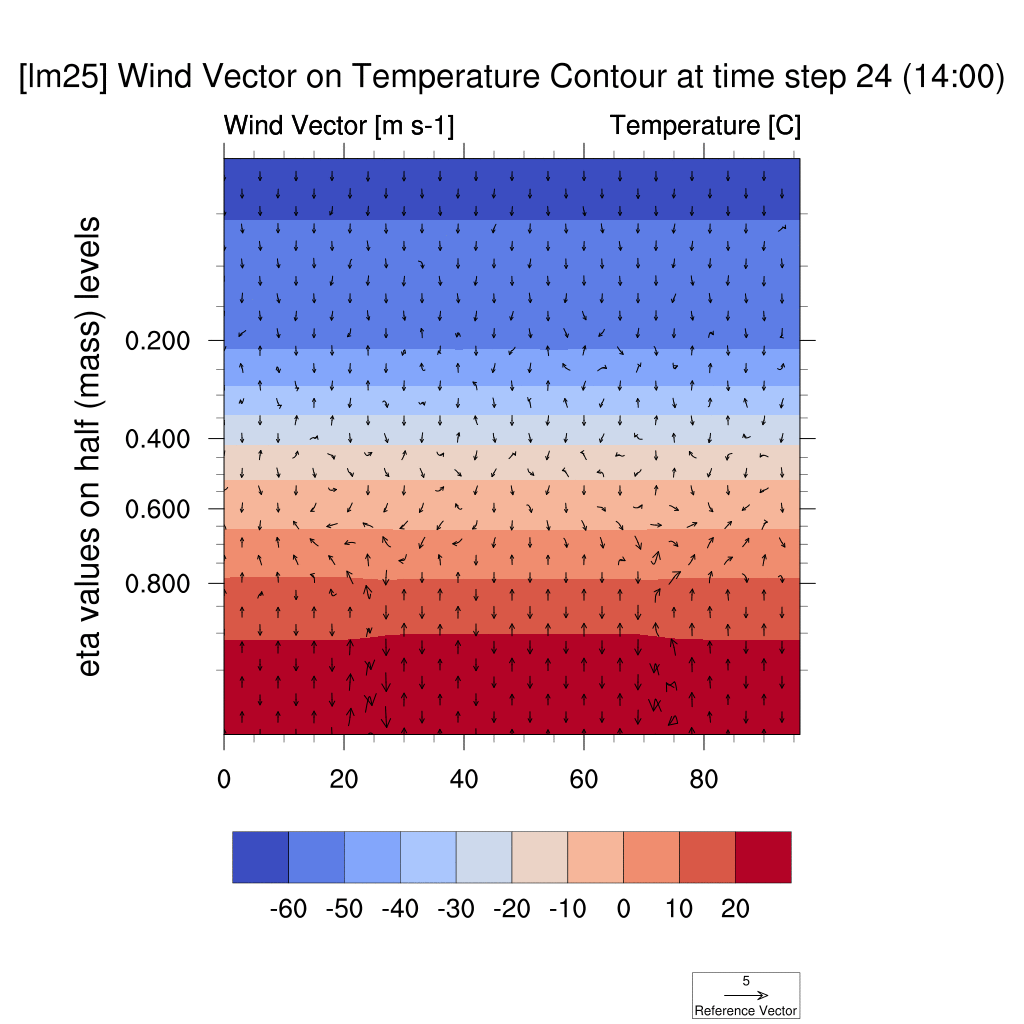

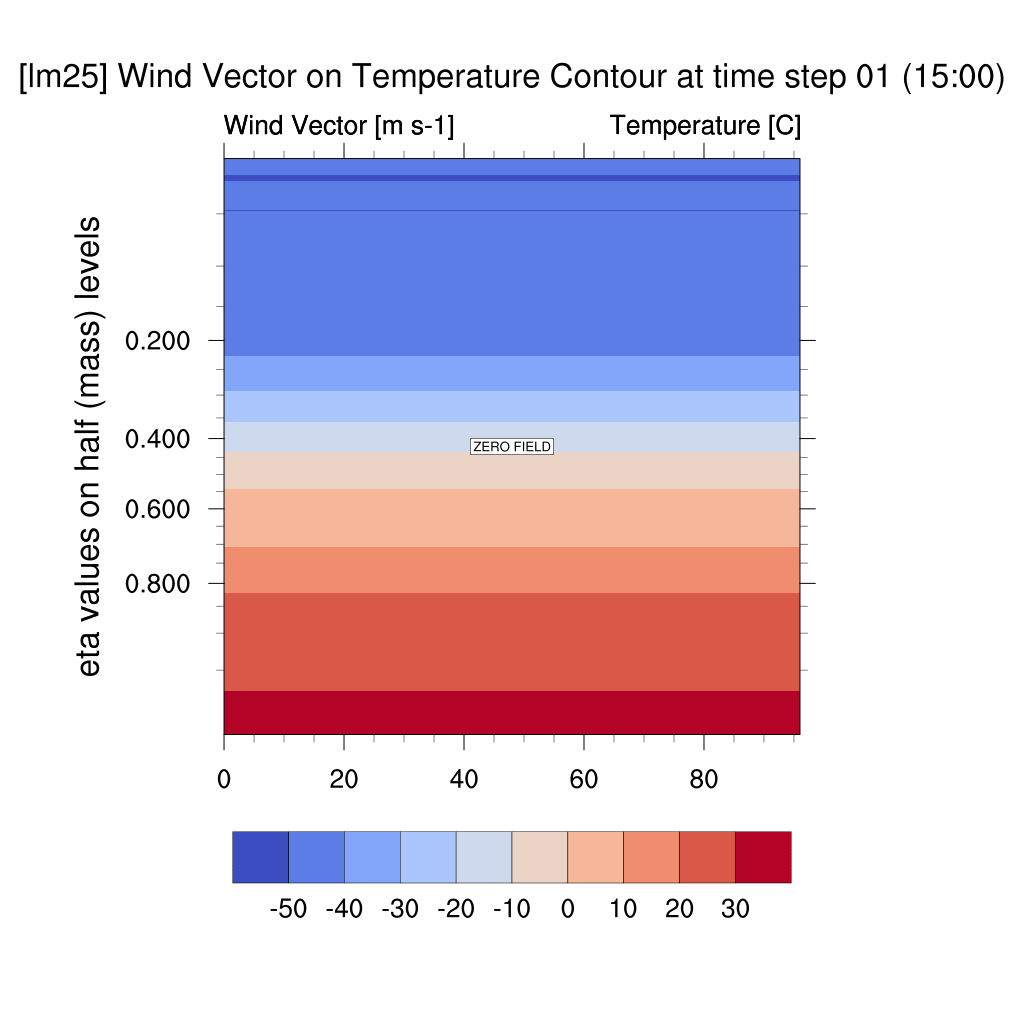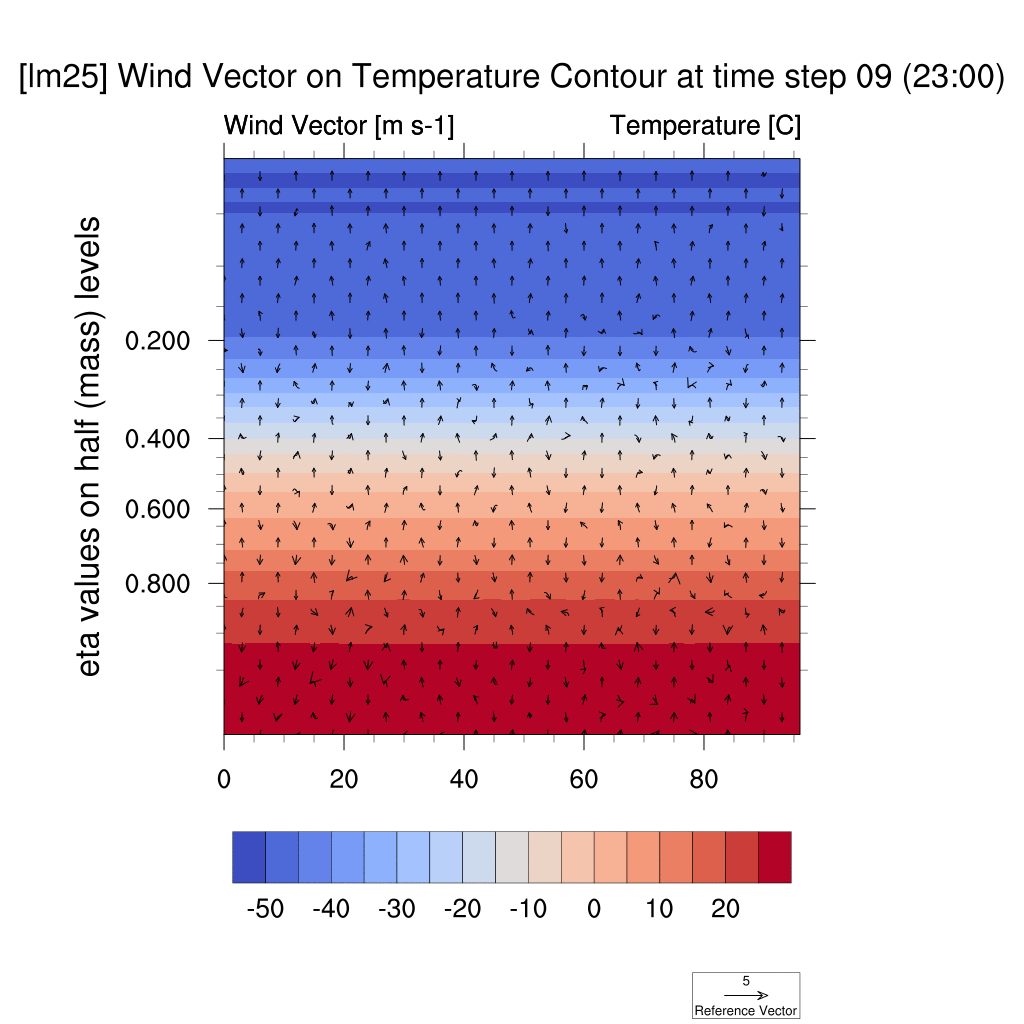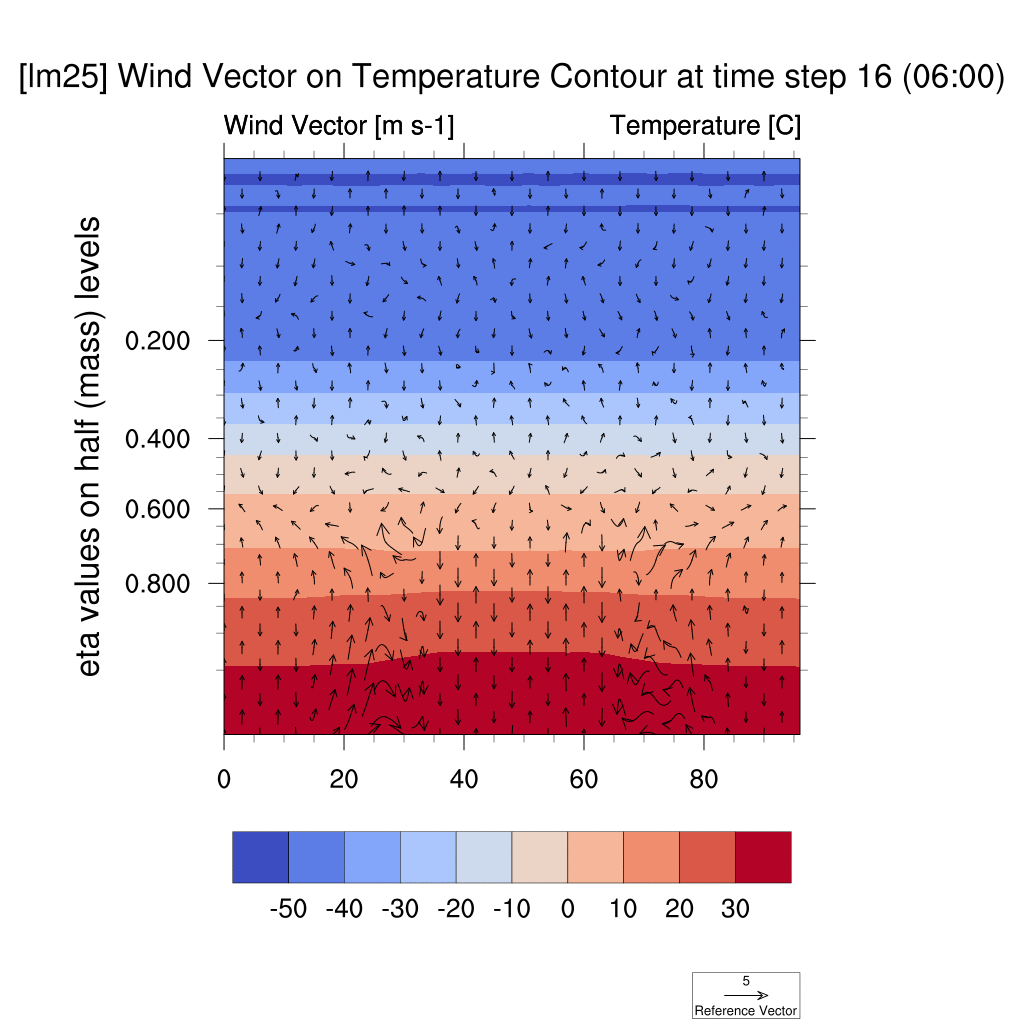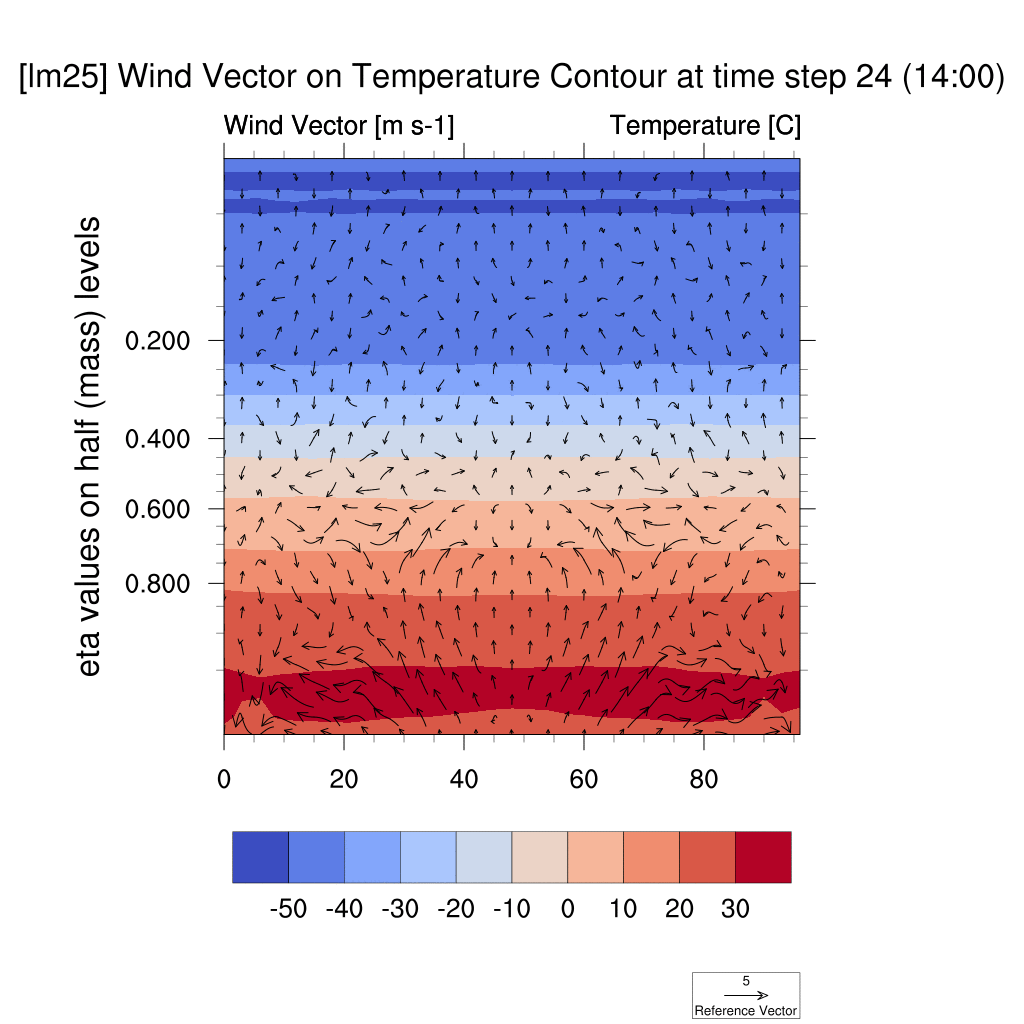
-
In both the SSP5-8.5 and SSP2-4.5 scenarios, atmospheric warming due to the urban heat island effect was observed; however, in the high-emission scenario, this effect was more pronounced, with stronger suppression of vertical convection and temperature increases compared to the low-emission scenario.
2. Vertical Temperature Contour
current (2024)
SSP2-4.5 (2100)
SSP5-8.5 (2100)



-
Under the SSP5-8.5 scenario, which represents a high greenhouse gas emissions pathway, a greater increase in temperature was observed compared to the SSP2-4.5 scenario, alongside a correspondingly stronger urban heat island effect.
-
Both scenarios exhibited temperatures exceeding current levels, and the intensity of the urban heat island effect was more pronounced in comparison to present-day conditions.
3. Wind Contour
- U wind (x-direction)
current (2024)
SSP2-4.5 (2100)
SSP5-8.5 (2100)
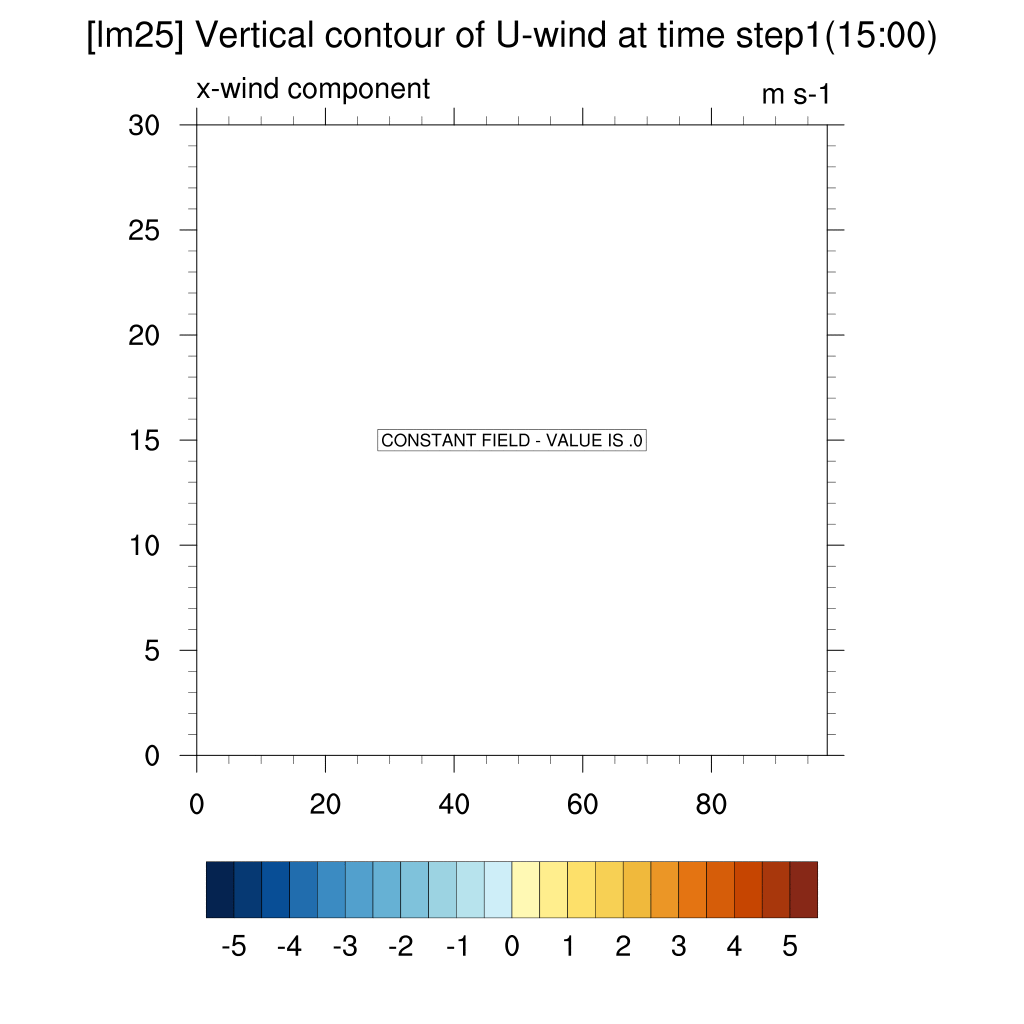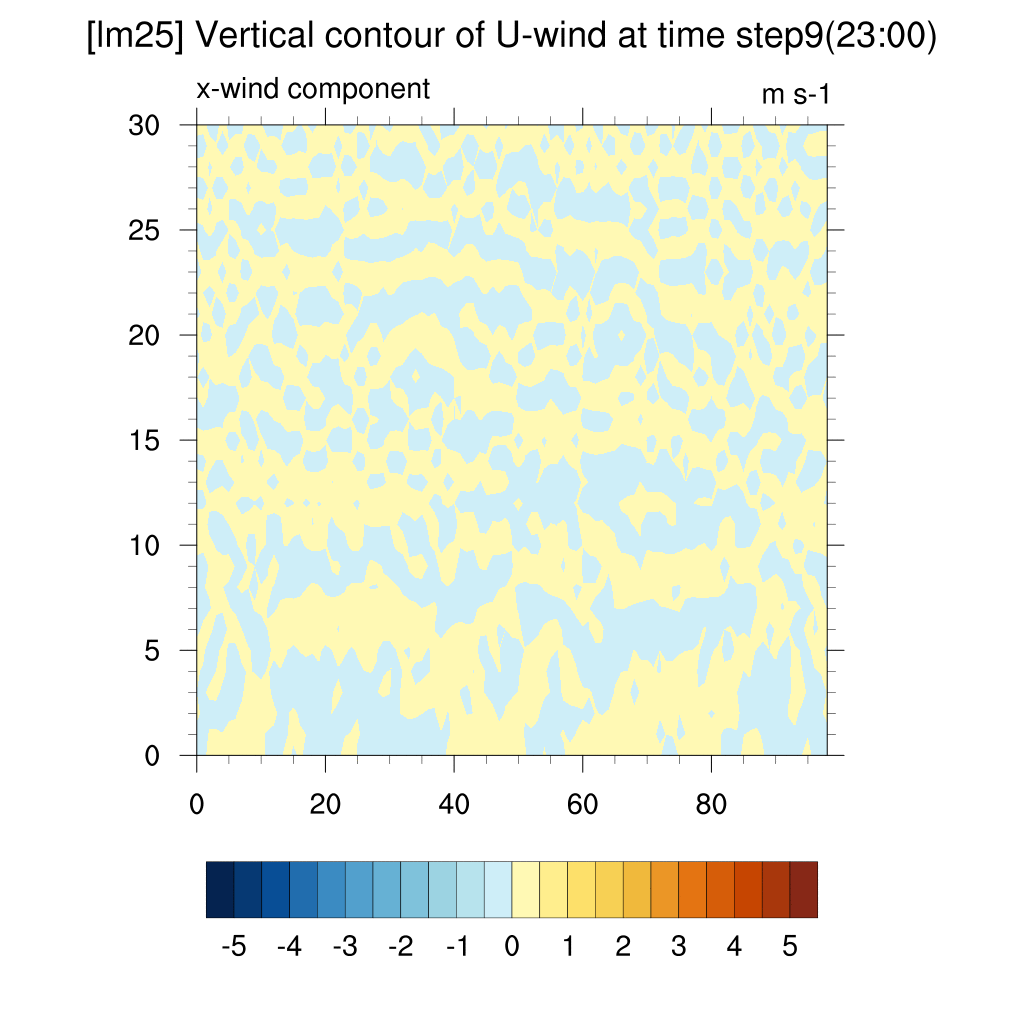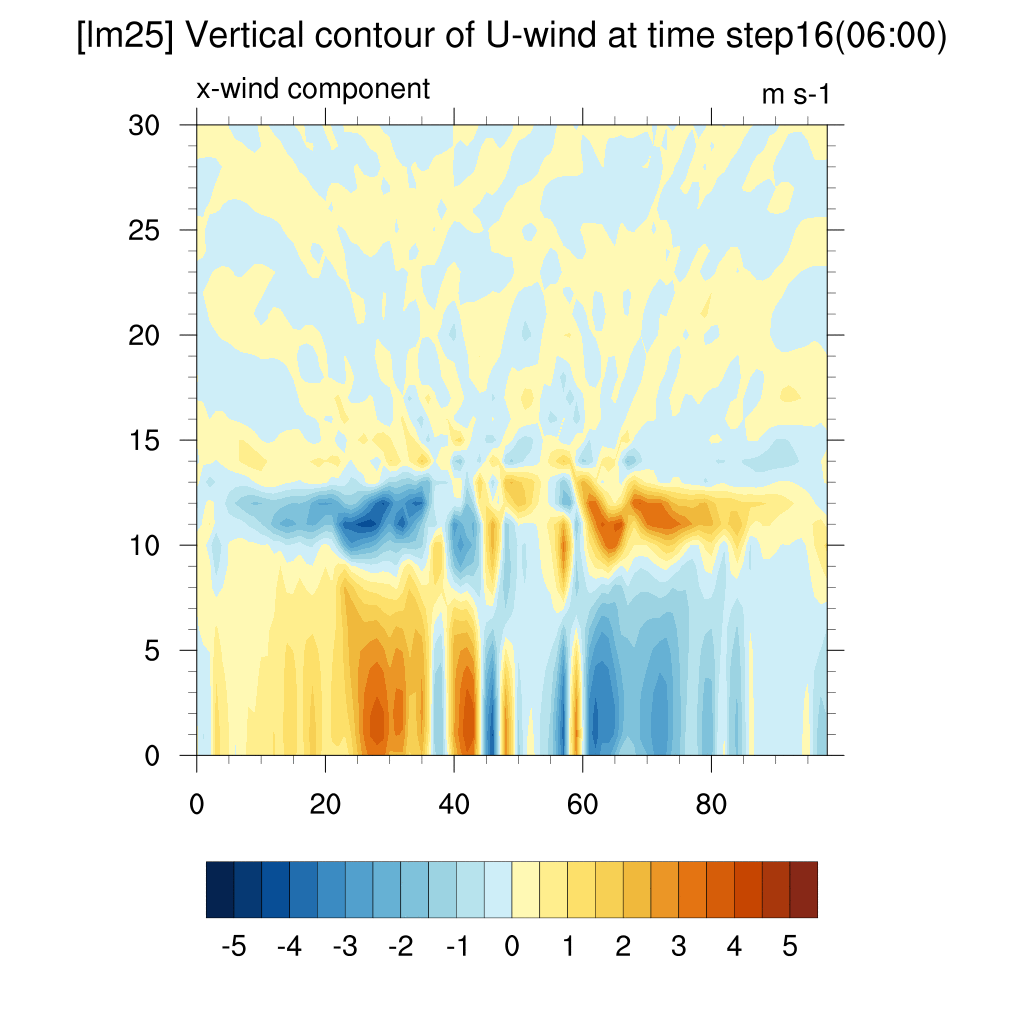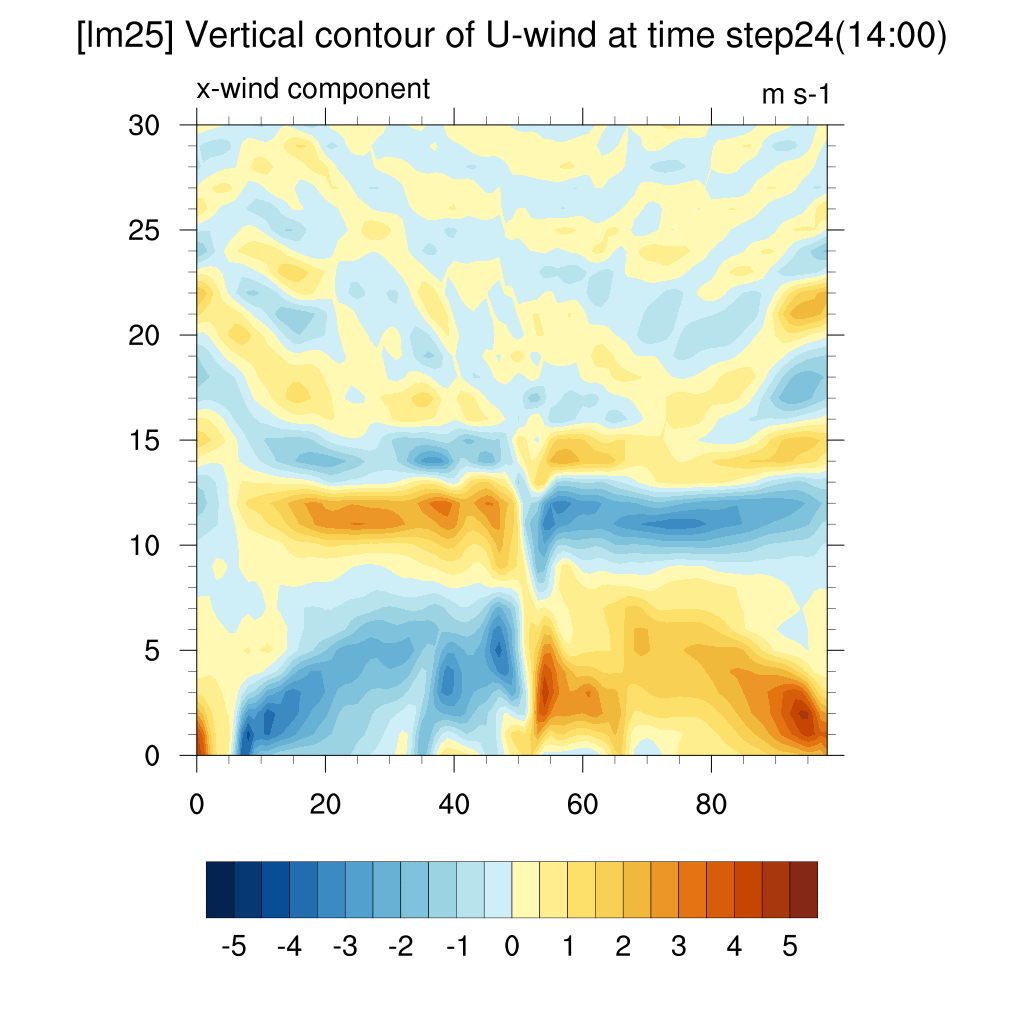


-
When comparing SSP2-4.5, SSP5-8.5, and the current case, both scenarios clearly show convergence compared to the present.
- W wind (z-direction)
current (2024)
SSP2-4.5 (2100)
SSP5-8.5 (2100)
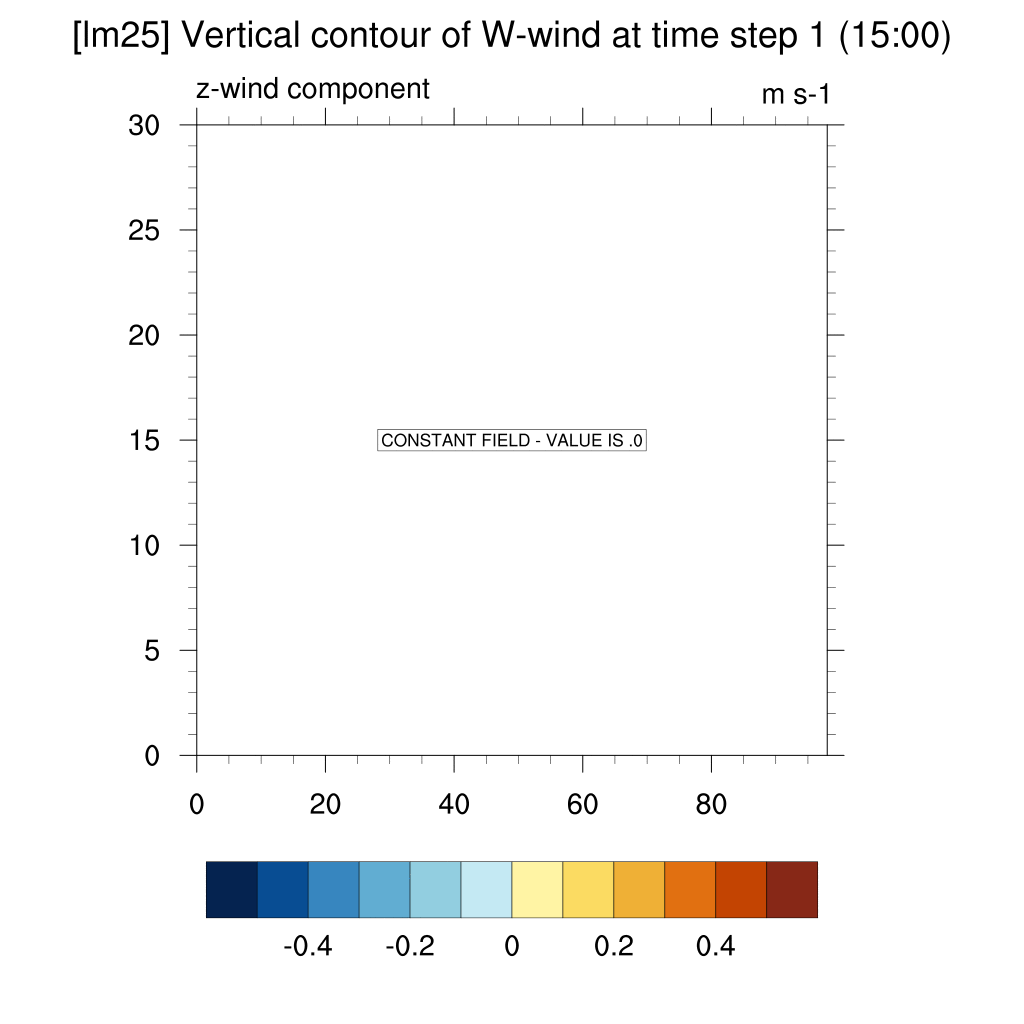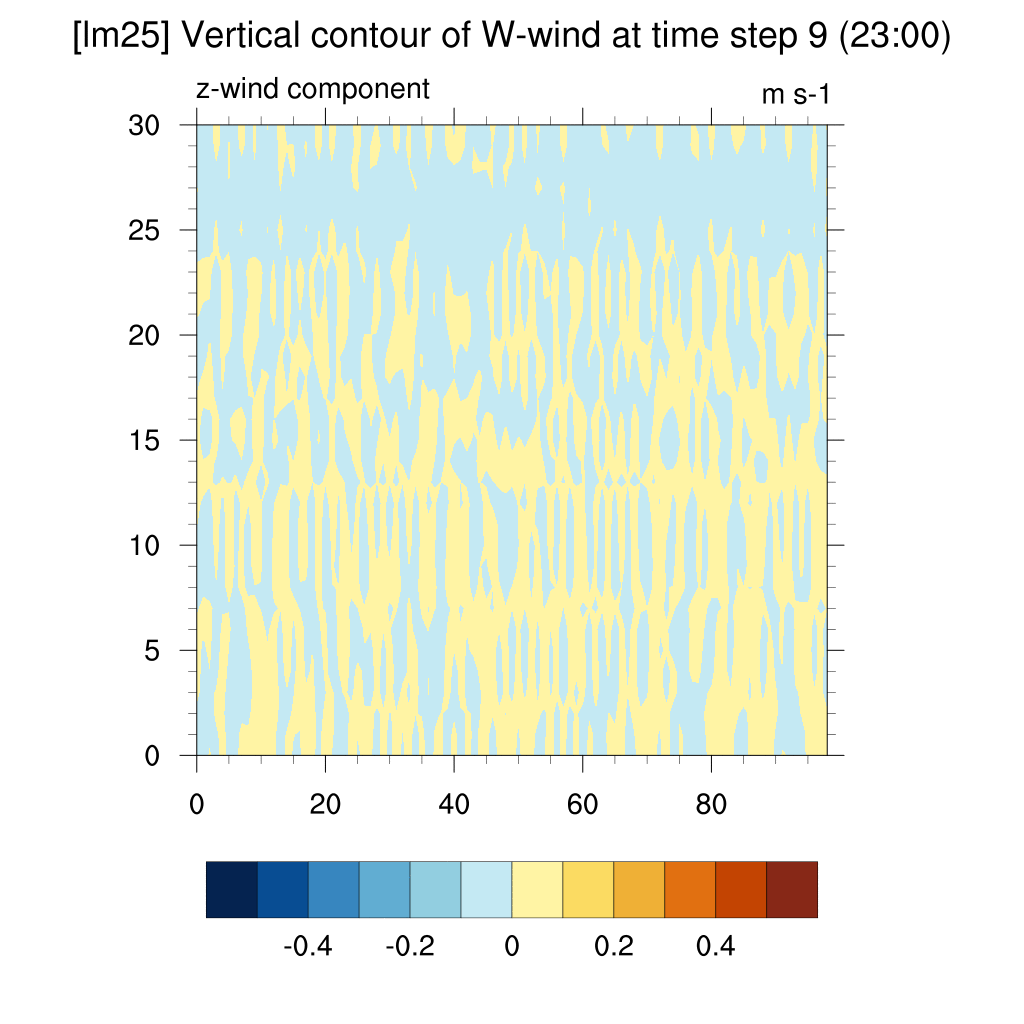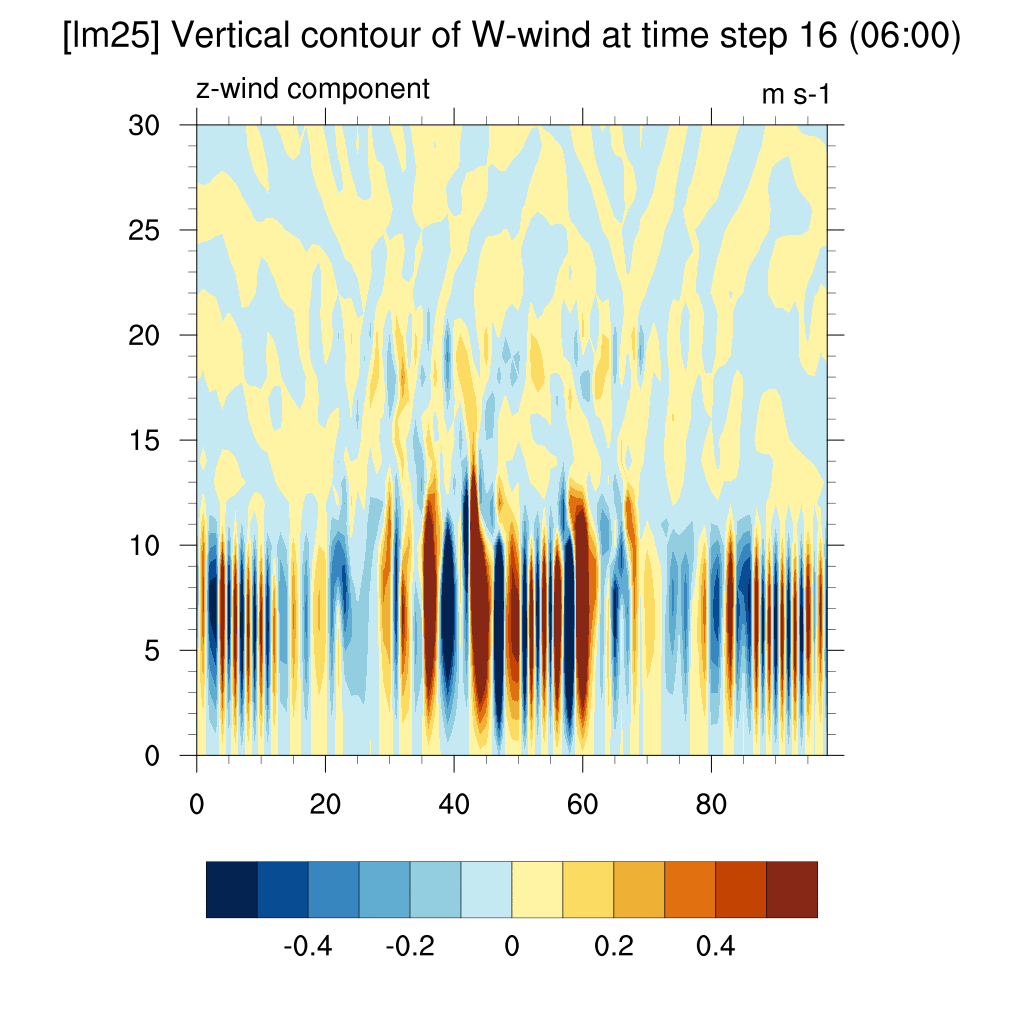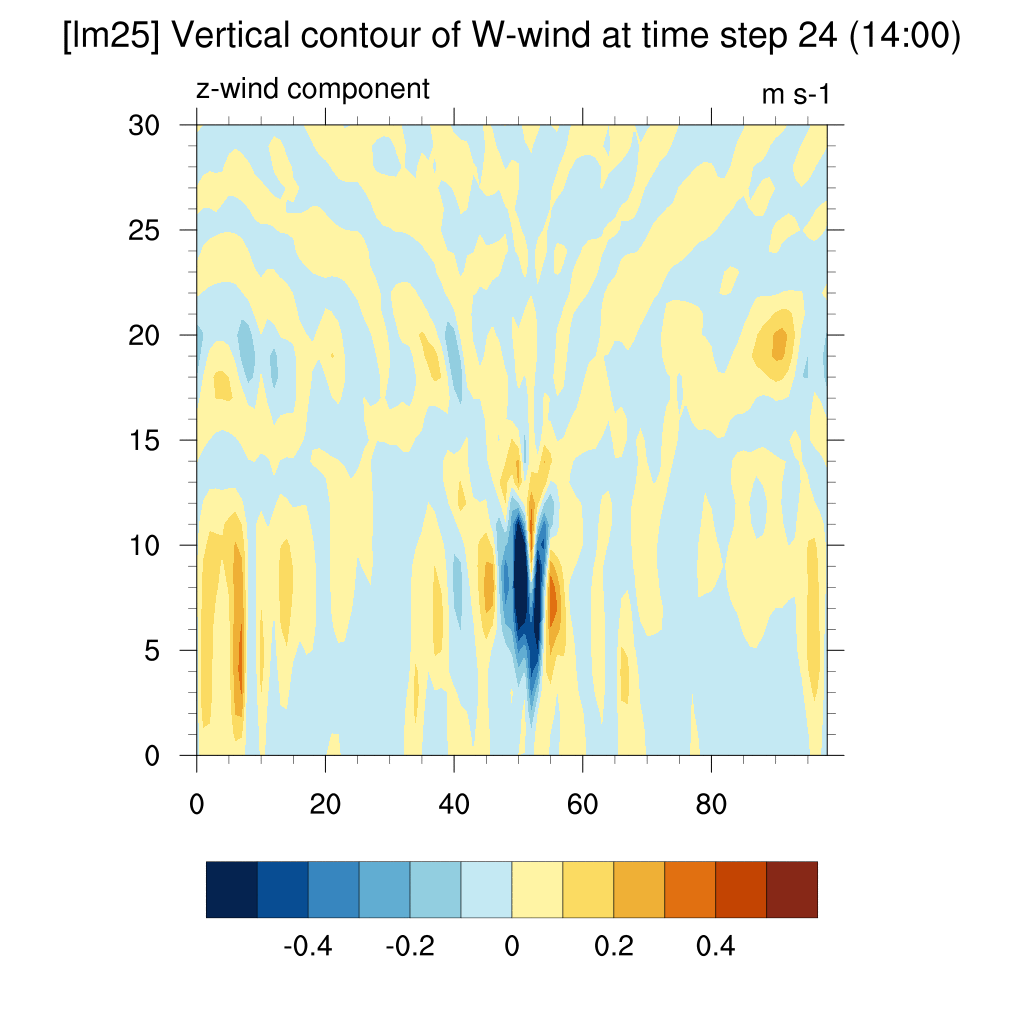
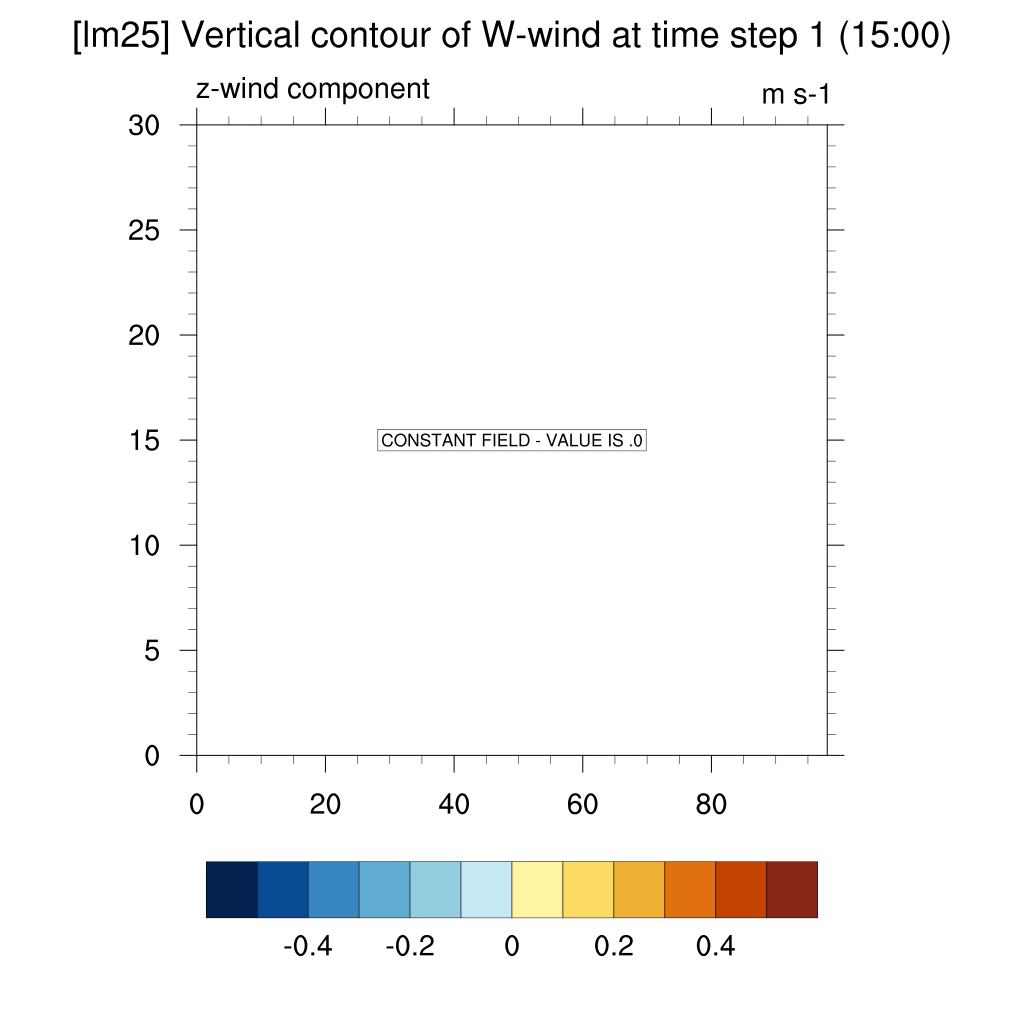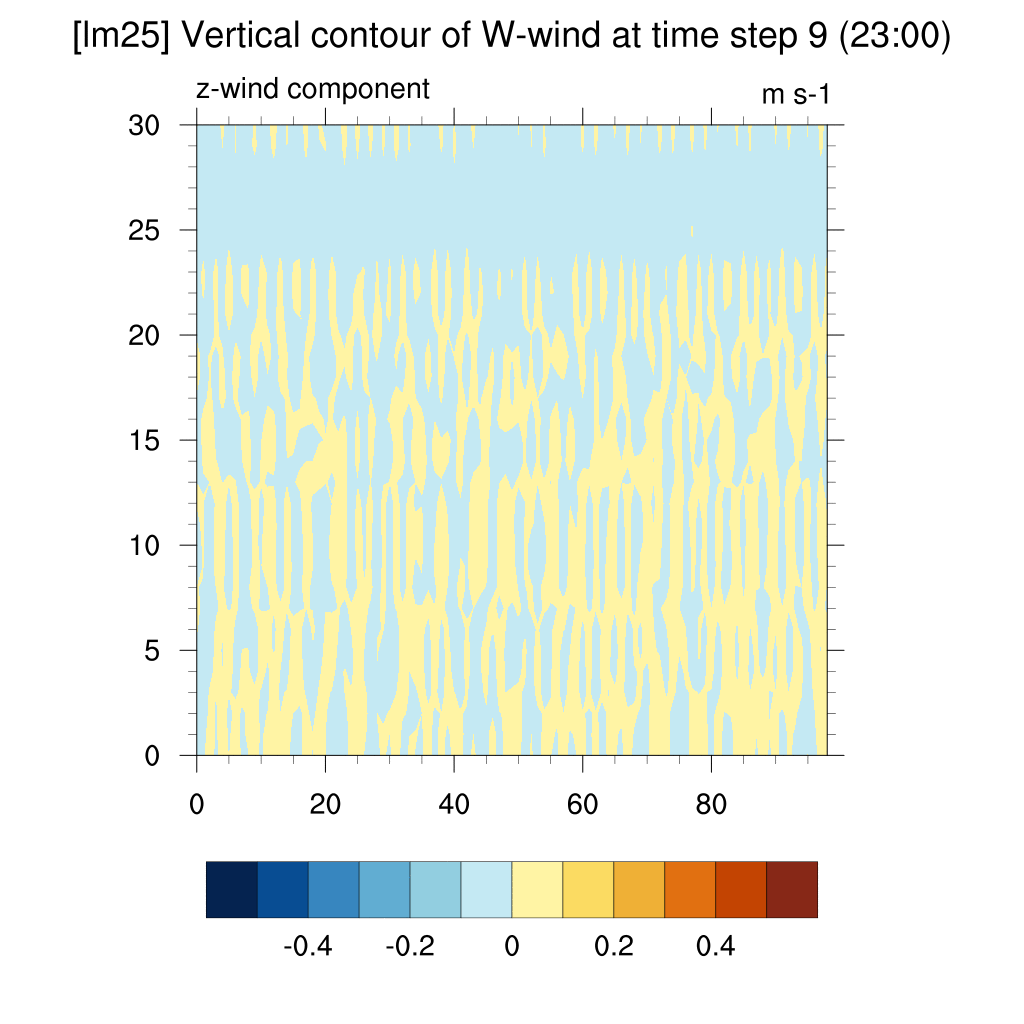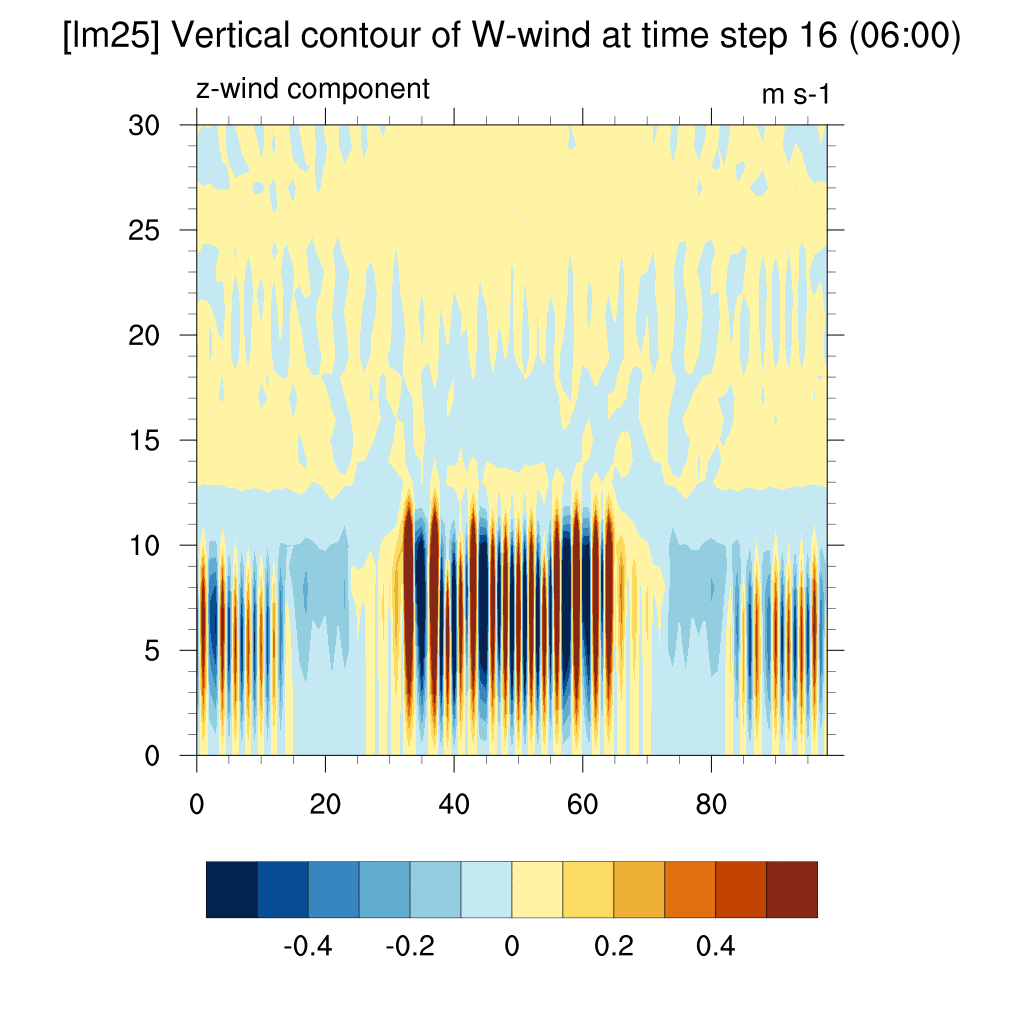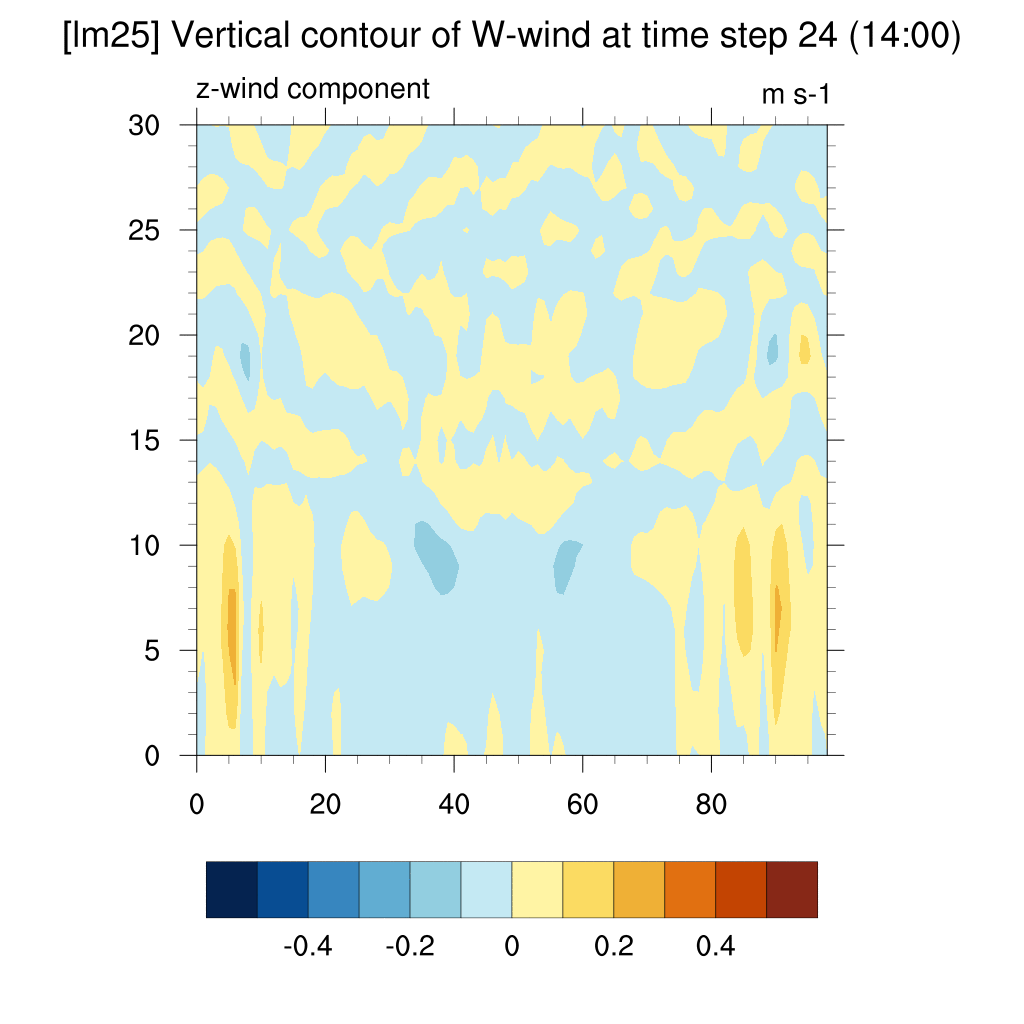

-
In the case of SSP scenarios, the upward flow area appeared more distinct above the dome shape. In contrast, for the current case, the dome shape quickly dissipated, and the upward flow above the dome was not clearly visible.
4. Average Temperature Series
current (2024)
SSP2-4.5 (2100)
SSP5-8.5 (2100)



-
Overall, the trend in the rate of change in average temperature appears similar, except for the current scenario in lm10. In the remaining SSP scenarios, the urban heat island effect is observed in all cases, with warming of approximately 3°C (SSP2-4.5) and 5°C (SSP5-8.5) at both altitudes compared to the present, based on the maximum values.
-
The similarity between the lm25 and lm40 curves in the SSP5-8.5 scenario is likely due to the use of the deviation method and the averaging process over latitude and longitude. This outcome reflects the non-linear nature of climate change, where temperature changes do not simply sum up but instead evolve in a complex manner.